How does Tersus handle long-range single baseline RTK positioning?
Lance Dong, Tersus GNSS 6 April, 2023
Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) has been known as one of the important tools for survey mapping, such as the most commonly used real-time kinematic (RTK) GNSS positioning method. As we all know, the RTK positioning method requires the rover station receiver in the user's hand to receive the differential data broadcast from the base station receiver to perform positioning calculations. However, the traditional RTK GNSS positioning method only guarantees a high-precision positioning solution (centimeter level) with a baseline length of less than 20 kilometers. However, when the base station is far away or a specific long-distance base station needs to be used, high-precision positioning becomes a greater challenge.
The main error sources affecting RTK accuracy are as follows:
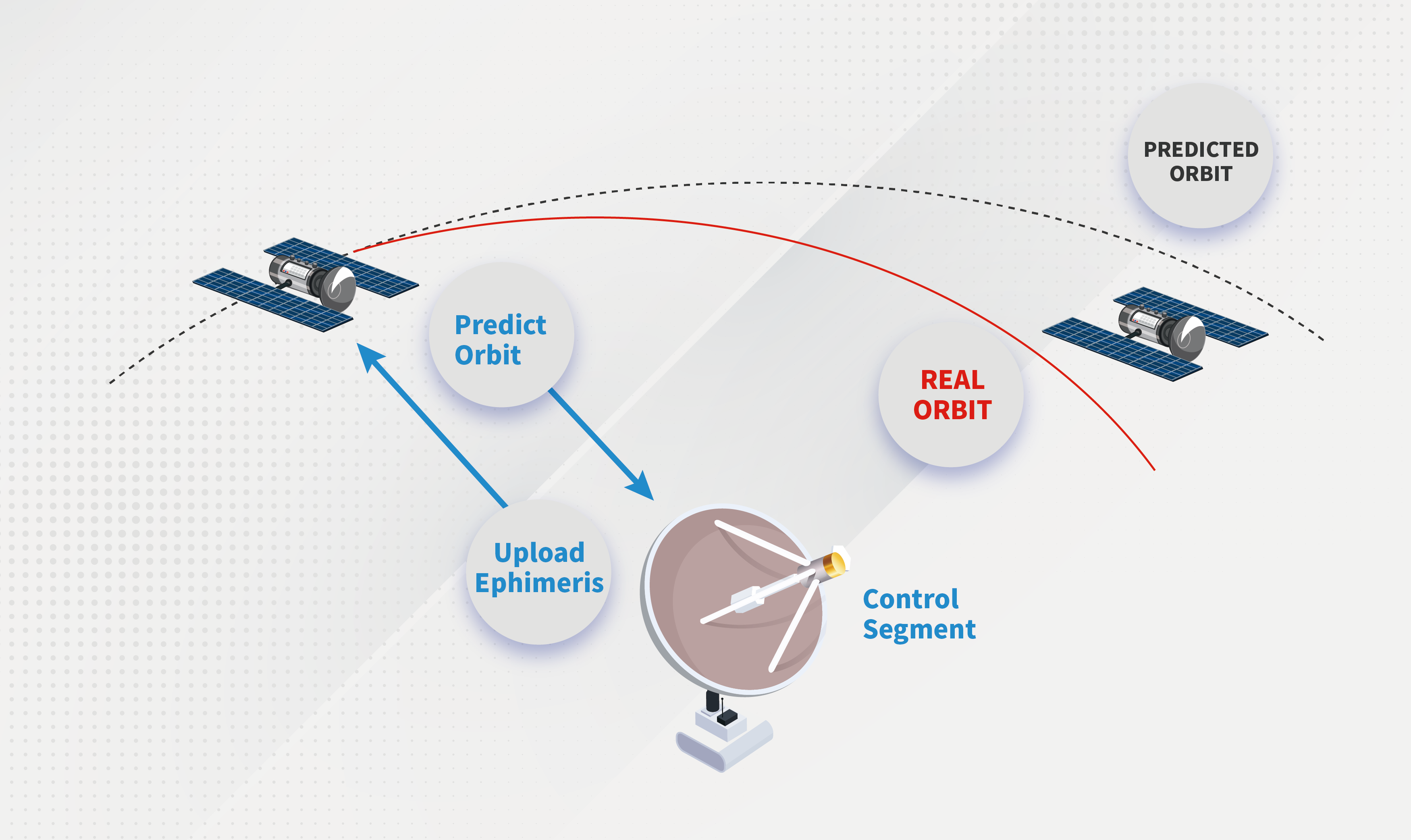
1. Orbit error· Satellite tracking capability
With the continuous improvement of orbit determination technology, the orbit error is only 5-10cm, and the relative error affecting the baseline is less than 1ppm.
2. Satellite clock error
At present, the clock error can be accurately determined through continuous monitoring of the operation status of satellite clocks. The impact of the clock error on the propagation distance will not exceed 6m, and the relative error of the baseline is about 0.2 ppm.
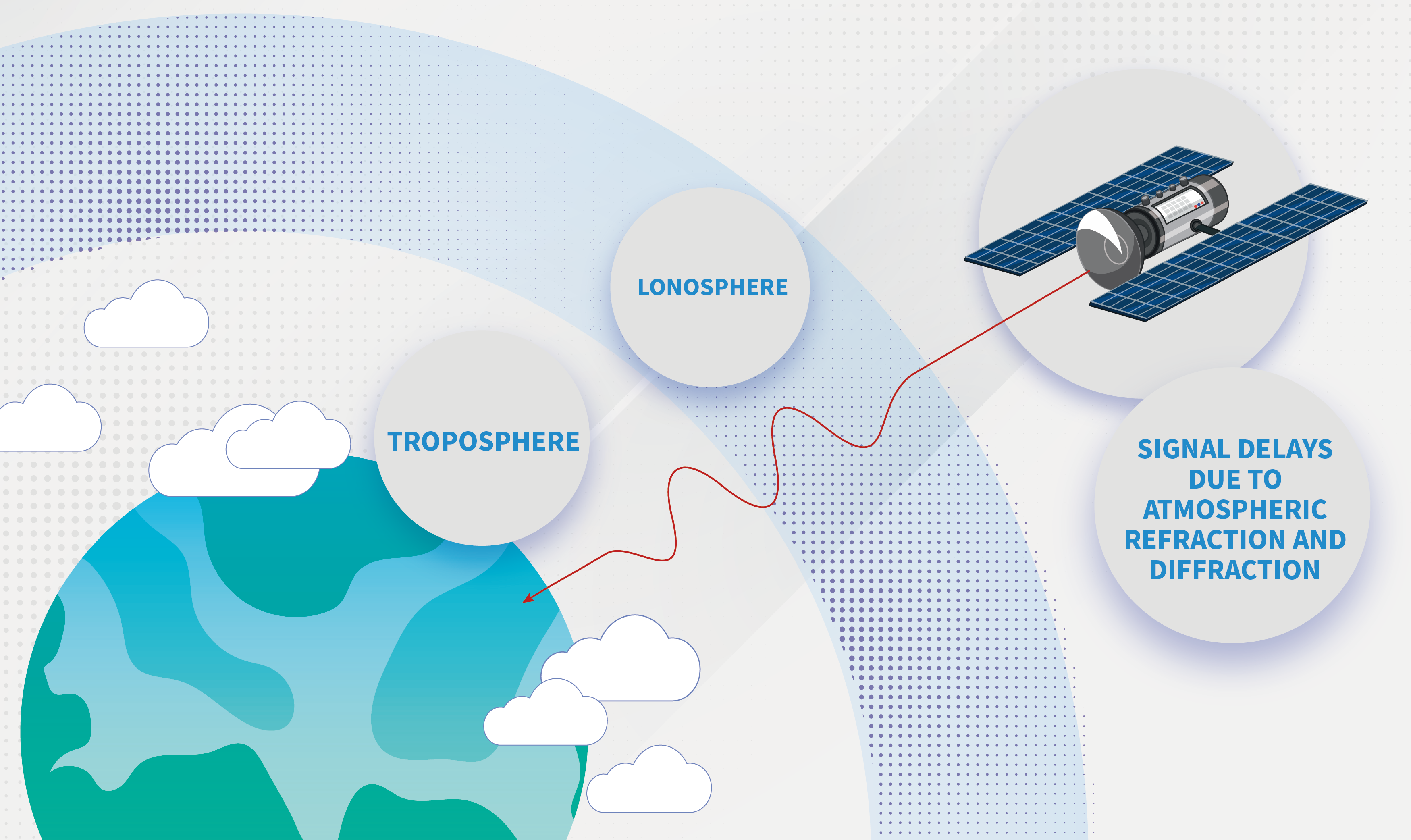
3. Ionospheric error
The ionosphere causes electromagnetic wave propagation delay to generate errors. The delay intensity is closely related to the electron density of the ionosphere. The electron density of the ionosphere varies with sunspot activity, geographical location, seasonal changes, and day and night. The error in the daytime is 5 times that of the nighttime, the error in winter is 5 times that of summer, and during the strongest sunspot activity, the error is 5 times that of the weakest time. During the sunspot eruption period, RTK measurement cannot be carried out.
4. Tropospheric error
The tropospheric error is closely related to the distance between points and the height difference between points. When the altitude angle is 90°, the propagation path difference of electromagnetic waves can reach 2-3mm, and when the altitude angle is 10, it can reach as high as about 20m.
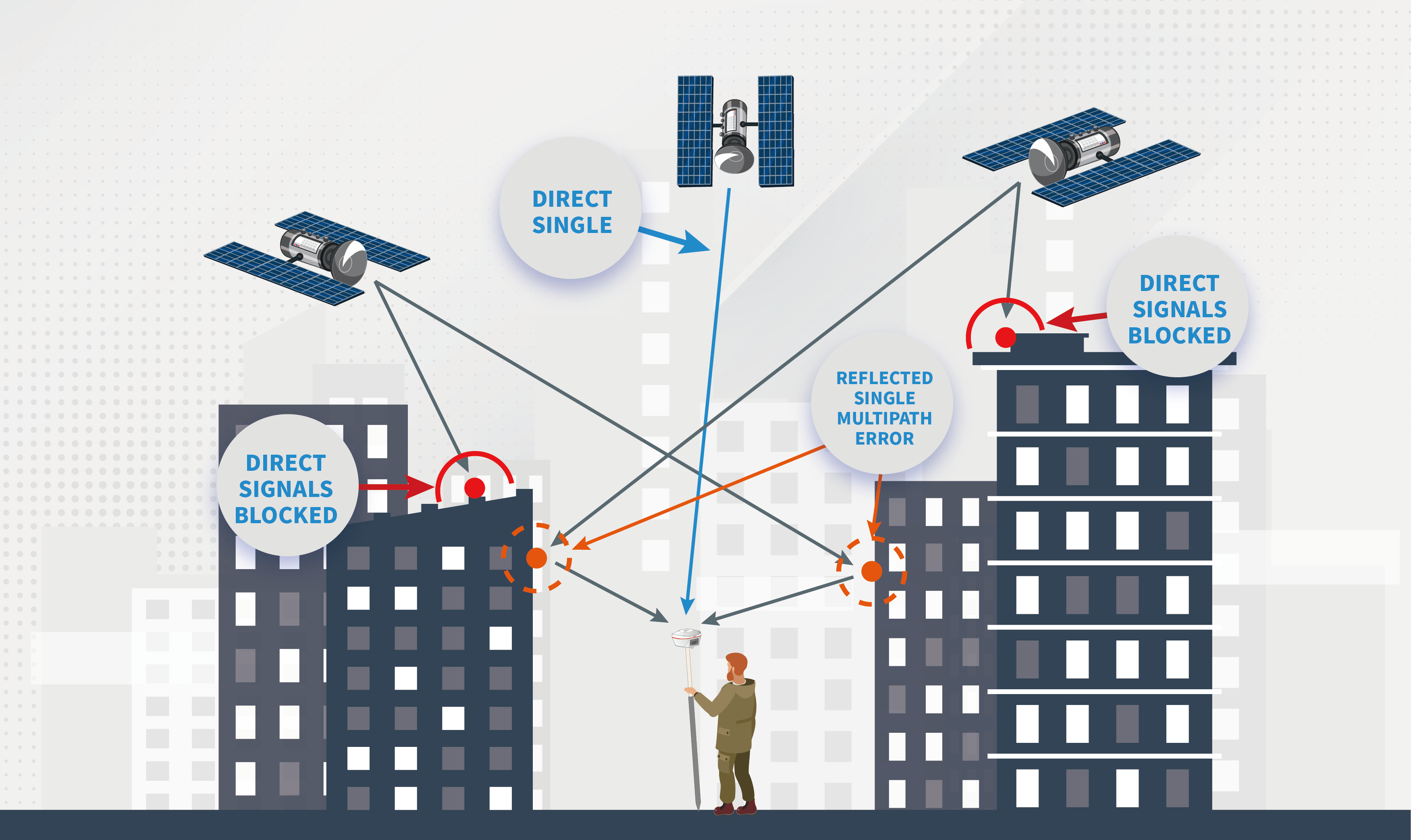
5. Multipath error
Multipath error is the most serious error in RTK positioning measurement. Multipath errors depend on the environment around the antenna. Multipath errors are typically a few centimeters and can exceed 10cm in highly reflective environments.
6. Signal Interference
Signal interference may have many causes, such as radio transmission sources, radar devices, high-voltage powerlines, etc. The strength of the interference depends on the frequency and the power of the transmitter, and the distance to the source of the interference.
The above errors all have a strong spatial correlation, and the influence has a certain positive correlation with the baseline length. So what are the main factors that cause significant errors in long-baseline measurements? How should we avoid and solve the impact of these error sources on the positioning results?
· For short baseline measurements of less than 10km, the impact of orbital errors and satellite errors can be ignored. But for long baseline measurements of 20-30km, orbital errors can reach 2-3cm.
· For the ionospheric error, use the dual-frequency receiver to linearly combine the observations of L1 and L2 to eliminate the influence of the ionosphere; use more than two observation stations to obtain the difference (short baseline); use the ionospheric model to add correction. The correction model has been added to the processing engine of Tersus Extreme RTK to correct the observation. When using the receiver to measure, the user should try to avoid the time period when the ionosphere is active. The real-time status of the global ionosphere can be viewed at http://ionosphere.cn.
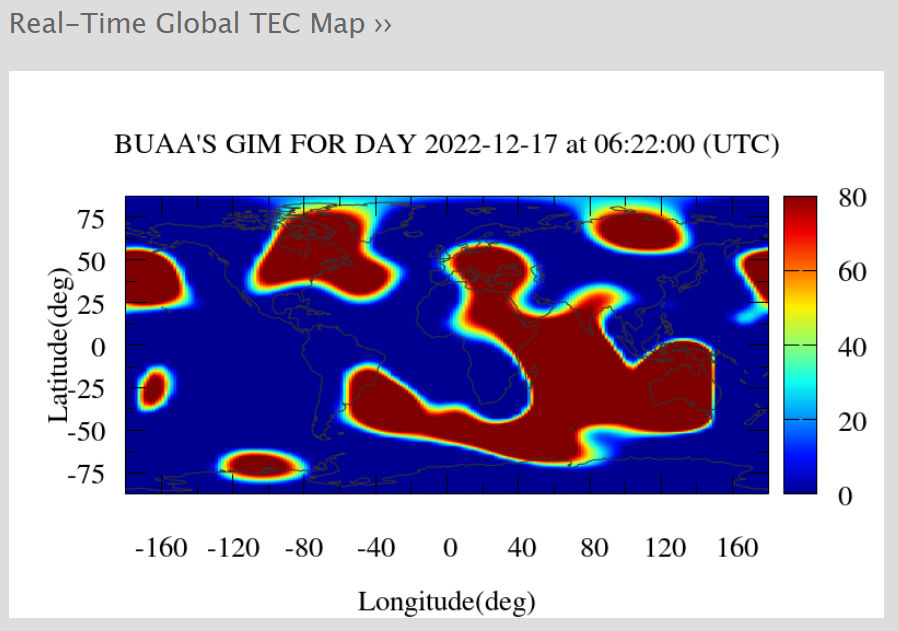
↑ The real-time status of the global ionosphere(Cr:http://ionosphere.cn)↑
· For the tropospheric error, the satellite altitude cut-off angle can be set to no less than 15, and the difference (short baseline) of the synchronous observations of more than two observation stations can be used to correct it. Also, the tropospheric model has already been used in the Tersus RTK engine.
· For multipath errors, it can be avoided by choosing an open area with no reflective surface; using choke coil antennas or antennas with various technologies to weaken multipath errors, and laying materials that absorb radio waves near the base station.
· For signal interference errors, it is necessary to stay away from these interference sources when selecting points. The distance from the radio transmitter should be more than 200m, and the distance from the high-voltage line should be more than 50m to effectively reduce the error.
Tersus has adopted various technologies at multiple aspects of hardware and processing engines to reduce the positioning impact caused by the above error sources. Taking the Oscar receiver as an example, the RTK accuracy is 8mm+1ppm horizontally and 15mm+1ppm vertically; corresponding to the 40km baseline as an example, the accuracy can be guaranteed at 48mm(8+1*40) horizontally and 55mm(15+1*40) vertically, which meets the measurement needs of users.
About Tersus GNSS Inc.
Tersus GNSS is a leading Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) solution provider. Our offerings and services aim to make centimeter-precision positioning affordable for large-scale deployment.
Founded in 2014, we have been pioneers in design and development GNSS RTK products to better cater to the industry’s needs. Our portfolios cover GNSS RTK & PPK OEM boards, David GNSS Receiver, Oscar GNSS Receiver, MatrixRTK [GNSS CORS Systems] and inertial navigation systems.
Designed for ease of use, our solutions support multi-GNSS and provide flexible interfaces for a variety of applications, such as UAVs, surveying, mapping, precision agriculture, lane-level navigation, construction engineering, and deformation monitoring.
Sales inquiry: sales@tersus-gnss.com
Technical support: support@tersus-gnss.com
